Institute of Chemistry, Academia Sinica – Research
利用蛋白水解靶向嵌合體(PROTACs)降解神經退化性疾病相關的TDP-43蛋白聚合物
Degradation of neurodegenerative disease-associated TDP-43 aggregates and oligomers via a proteolysis-targeting chimera
J. Biomed. Sci. 2023, 30, 27.
Yu-Ling Tseng, Po-Chao Lu, Chi-Chang Lee, Ruei-Yu He, Yung-An Huang, Yin-Chen Tseng, Ting-Jen Rachel Cheng, Joseph Jen-Tse Huang* & Jim-Min Fang*
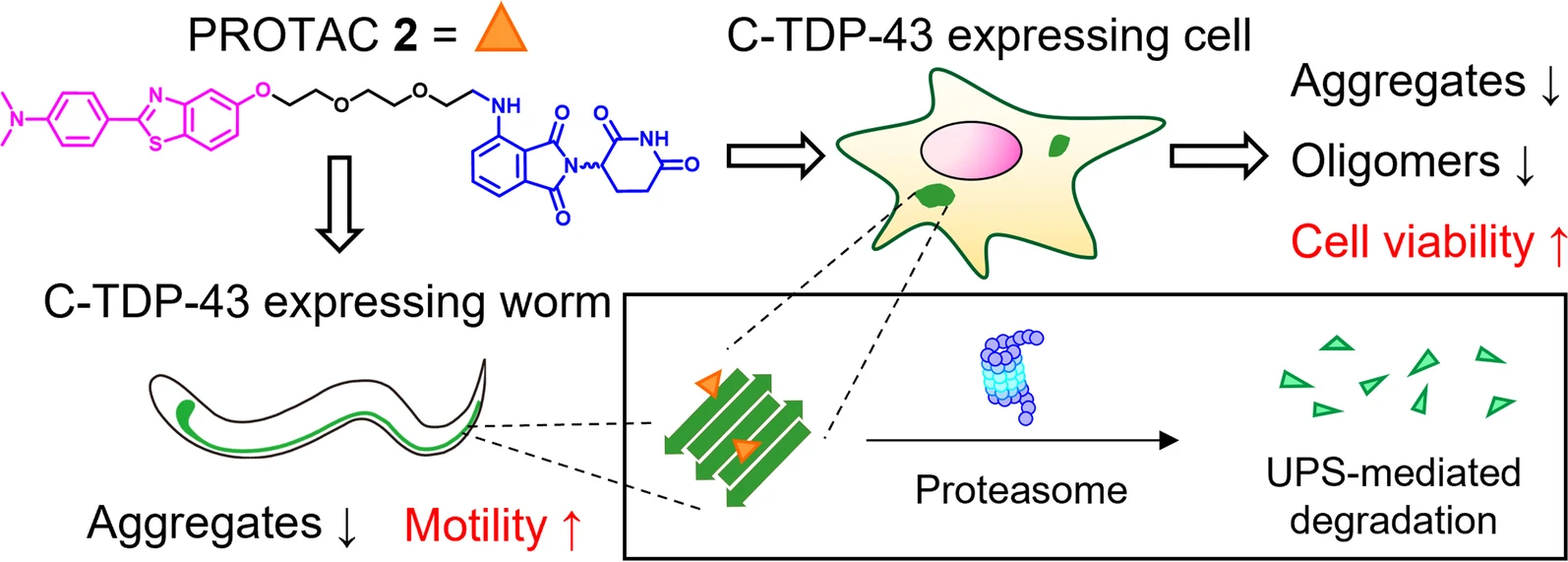
近年來,與神經退化性疾病有關的錯誤摺疊蛋白,因為老化議題而受到廣泛的關注。在臨床上,可觀察到病人神經組織切片中錯誤摺疊蛋白有聚集的現象。然而,造成神經退化性疾病的聚集物一直以來都被認為是傳統抑制劑或拮抗劑無法針對的目標,因此,許多神經退化疾病的研究開始設計一些能夠清除錯誤摺疊蛋白聚集物的藥物(如清除 TDP-43 聚集物)。事實上,近年來 TDP-43 的聚集物也被視為判定肌萎縮性脊髓側索硬化症(ALS)與額顳葉失智症(FTLD)的指標蛋白。為了提供這樣的需求,我們與台灣大學化學系方俊民老師共同合作開發了一系列的蛋白水解靶向嵌合體(PROTACs)來清除 TDP-43 聚集物。在本篇研究中,我們利用在細胞中表達 TDP-43 聚集物的方式建立 PROTAC 化合物的篩選平台。透過這個平台,我們證明了 PROTAC 2 可與 TDP-43 聚集物結合。同時,我們也證實了 PROTAC 2 可以減少細胞中的 TDP-43 聚集物,以提高神經細胞的存活率。我們更透過了先進的顯微影像技術,進一步的證明 PROTAC 2 同時也降低了 TDP-43 寡聚體(oligomers)的數量。最後,我們觀察到 PROTAC 2 不僅可以減少線蟲(C. elegans)神經細胞中的 TDP-43 聚集物數量,也可以同時改善線蟲的運動能力。總括來說,我們的研究證明了新設計的 PROTAC 2 對於 TDP-43 聚集物與寡聚體具有雙重靶向能力,並增加細胞存活率,改善實驗動物的運動能力,為開發 ALS 以及其他神經退行性疾病的藥物提供了新的方向。
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) associated with TAR DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43) aggregation has been considered as a lethal and progressive motor neuron disease. Recent studies have shown that both C-terminal TDP-43 (C-TDP-43) aggregates and oligomers were neurotoxic and pathologic agents in ALS and frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD). However, misfolding protein has long been considered as an undruggable target by applying conventional inhibitors, agonists, or antagonists. To provide this unmet medical need, we aim to degrade these misfolding proteins by designing a series of proteolysis targeting chimeras (PROTACs) against C-TDP-43. We showed that PROTAC 2 bound to C-TDP-43 aggregates and E3 ligase to initiate ubiquitination and proteolytic degradation. By applying advanced microscopy, it was further shown that PROTAC 2 decreased the compactness and population of C-TDP-43 oligomers. In addition to cellular model, PROTAC 2 also improved the motility of transgenic C. elegans by reducing the C-TDP-43 aggregates in the nervous system. Our study demonstrated the dual-targeting capacity of the newly-designed PROTAC 2 against both C-TDP-43 aggregates and oligomers to reduce their neurotoxicity, which shed light on the potential drug development for ALS as well as other neurodegenerative diseases.
