Institute of Chemistry, Academia Sinica – Research
Titanosilicates with Strong Phase-Matched Second Harmonic Generation Responses
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 9061-9064. DOI: 10.1021/jacs.6b05327
Tzu-Ling Chao, Wen-Jung Chang, Shu-Han Wen, Yu-Qing Lin, Bor-Chen Chang,* and Kwang-Hwa Lii*
尋找新的而且有用的非線性光學晶體一直是一個重要的研究課題,主要原因是這種材料在雷射科技上有很大的應用價值。雖然許多氧化物、磷酸鹽、硼酸鹽、含氟硼酸鹽倍頻材料被發現,但是具有應用價值的矽酸鹽非線性光學晶體尚未發現。在這篇論文中我們利用熔鹽法與超臨界水熱法合成兩個矽酸鈦,並且生長大晶體。此二化合物具有新穎的三維結構,包含壓縮的TiO5五面體,排列形成···Ti-O···Ti-O直鏈,其中Ti-O距離一長一短。這兩個材料的性質滿足具有應用價值非線性光學材料的條件包括非中心對稱、大的非線性係數、相位匹配、應用光學區段透明、高雷射損傷閥值、熱穩定性等,因此是兩個非常具有應用價值與發展潛力的倍頻材料。
The search for new and efficient nonlinear optical (NLO) materials has been an active research because of their technological importance in laser applications. Although a large number of frequency-doubling oxides, phosphates, borates, and fluoride-containing borates were found, no transition metal silicate with useful NLO properties has been reported. We have now synthesized and grown crystals of two new titanosilicates, Li2K4[(TiO)Si4O12] and Li2Rb4[(TiO)Si4O12], by using a flux and supercritical hydrothermal method. Their unique 3D framework structures contain highly compressed TiO5 square pyramids which are arranged one over the other to form infinite ···Ti–O···Ti–O straight chains with alternating short and long Ti-O distances. These two materials meet the requirements for efficient second harmonic generation including lack of center of inversion symmetry, large susceptibility, phase matching, transmitting at wavelengths of interest, resistant to laser damage, and thermally stable. These attributes make them very attractive for frequency doubling materials.
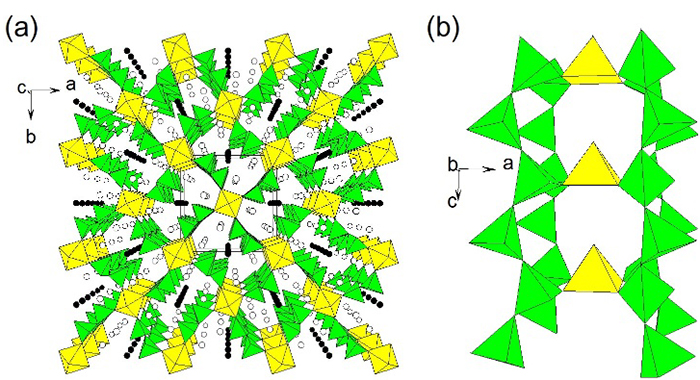
Figure.
(a) Perspective view of the structure of Li2K4[(TiO)Si4O12] along the c axis. Key: Yellow square pyramid, TiO5; green tetrahedron, SiO4; solid circle, Li; open circle, K.
(b) Section of the structure viewed along the b axis showing the connectivity between TiO5 and silicate chains.
