中央研究院化學研究所-學術研究
利用鋰化矽醚類化合物建構苯環上鄰位羥基之酮類化合物
Lithiation of a Silyl Ether; Formation on an ortho-Fries HydroxyketoneAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, Early View Article. ( Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 1-5)
DOI: 10.1002/anie.201404495R1 and 10.1002/ange.201404495R1
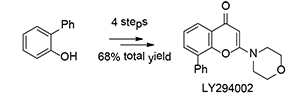
藉由苯環鄰位定向基團的導引,二異丙基氨基鋰可選擇性鋰化烷基矽氧上的 a-質子,繼以發生分子內親核取代反應達成 "矽→碳" 烷基轉移的效果。這個方法突破了長久以來矽醚保護基的單一用途,並開啟矽醚類化合物在有機合成上的新發展。在本研究中,我們進一步拓展此反應的應用性,開發出陰離子性 Snieckus-Fries 重排的延伸反應。此官能基轉換包含了三個重要概念:(1) 利用錯合物引導的概念進行去質子化步驟;(2) a-矽基碳陰離子和醯胺基間進行分子內 Peterson 類型反應;(3) β-含氧矽化物中間體的快速降解。此方法更可進一步應用在天然物合成中,縮短合成路徑以提升合成效率,如 PI3K 抑制劑 LY294002 的合成 (以鄰苯基苯酚為起始物經四步得到 LY294002,總產率 68%)。
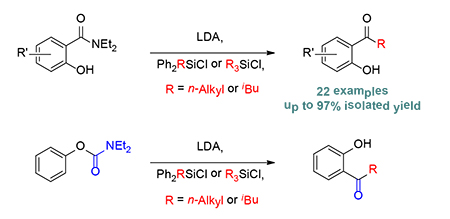
The hydroxy-directed nucleophilic acyl alkylation of hydroxyarylamides and salicylic acid through an anionic Si→C alkyl migration was developed using a simple reagent combination of LDA and chlorosilane. The transformation involves (1) a complex-induced proximity effect (CIPE) in the deprotonation step, (2) an intramolecular Peterson type reaction of the resulting a-silyl carbanion with the amide group, and (3) fission of the final β-oxygenated silyl intermediate. This reaction giving silyl ether a new role in organic synthesis was further developed for application to an extended anionic Snieckus-Fries rearrangement. The exceptional functional group transformations achievable using a simple reagent combination of LDA and chlorosilane renders these reactions highly valuable for the synthesis of natural products and medicinally important compounds, such as the PI3K inhibitor LY294002.
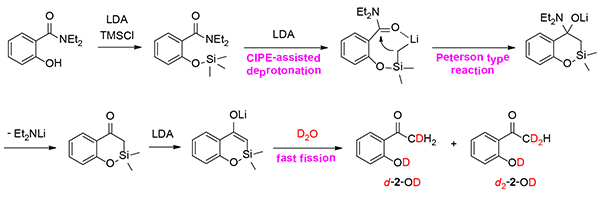
Plausible reaction mechanism of the ortho-directed nucleophilic acyl methylation of a hydroxyarylamide (arrows may be considered equilibria) and the D2O quenching experiment.