Institute of Chemistry, Academia Sinica – Research
醣啟動了調控活化B細胞存亡之樞紐
Temporal regulation of Lsp1 O-GlcNAcylation and phosphorylation during apoptosis of activated B cells
Nat Commun. 2016, 7, 12526.
Wu JL, Wu HY, Tsai DY, Chiang MF, Chen YJ, Gao S, Lin CC, Lin CH, Khoo KH, Chen YJ, Lin KI
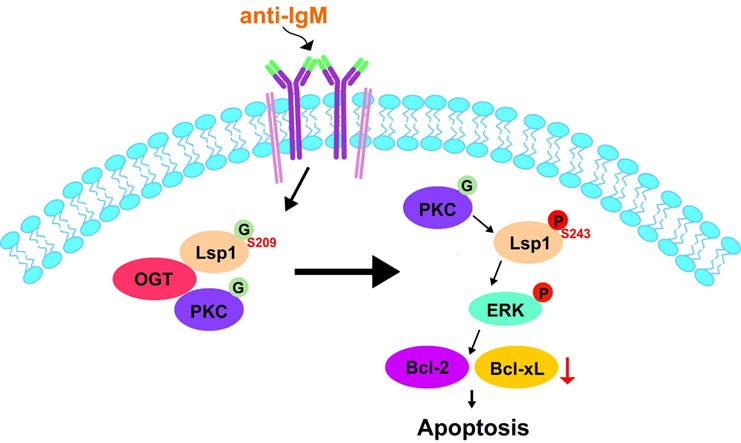
O連結乙醯葡萄氨糖修飾是細胞中的一種後轉錄調控修飾作用,在細胞中此種修飾是經由OGT酵素在蛋白質的絲氨酸和蘇氨酸進行催化完成,另一個酵素OGA則負責將此修飾移除。由於此種修飾是發生在絲氨酸和蘇氨酸上,其在細胞中所參與的許多作用被認為是藉由影響磷酸化修飾來達成。磷酸化蛋白質體和O 連結乙醯葡萄氨糖修飾之同時分析,我們發現高達313個磷酸化點位受到乙醯葡萄氨糖之影響, 其中,Lsp1 蛋白會被 O 連結乙醯葡萄氨糖修飾在絲氨酸 209 位點上。並進而啟動絲氨酸 243 位點的磷酸化透過 Lsp1 蛋白不同的後轉譯修飾突變進行功能性分析時,我們觀察到 Lsp1 蛋白的 O 連結乙醯葡萄氨糖修飾和絲氨酸 243 位點的磷酸化會調控B 細胞的細胞凋亡作用之重要機制,實驗結果發現Lsp1 蛋白的 O 連結乙醯葡萄氨糖修飾是藉由增加 Lsp1 蛋白和負責絲氨酸 243 位點的磷酸化之激酶,PKC-β1 的接合量來達成促進下游和細胞凋亡相關的訊息傳遞體之活化,及降低BCL-2 和 BCL-xL 的表現來達成促進細胞凋亡的作用。綜合上述,我們的實驗結果闡述了蛋白 O 連結乙醯葡萄氨糖修飾和磷酸化修飾之間的動態交互作用決定了 B 細胞受受體接合而活化後的細胞凋亡命運。
Crosslinking of B-cell receptor (BCR) sets off an apoptosis programme, but the underlying pathways remain obscure. Here we decipher the molecular mechanisms bridging B-cell activation and apoptosis mediated by post-translational modification (PTM). We find that O-GlcNAcase inhibition enhances B-cell activation and apoptosis induced by BCR crosslinking. This proteome-scale analysis of the functional interplay between protein O-GlcNAcylation and phosphorylation in stimulated mouse primary B cells identifies 313 O-GlcNAcylation-dependent phosphosites on 224 phosphoproteins. Among these phosphoproteins, temporal regulation of the O-GlcNAcylation and phosphorylation of lymphocyte-specific protein-1 (Lsp1) is a key switch that triggers apoptosis in activated B cells. O-GlcNAcylation at S209 of Lsp1 is a prerequisite for the recruitment of its kinase, PKC-β1, to induce S243 phosphorylation, leading to ERK activation and downregulation of BCL-2 and BCL-xL. Thus, we demonstrate the critical PTM interplay of Lsp1 that transmits signals for initiating apoptosis after BCR ligation.